41 labeling nucleotide examples
DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides Probe labeling process radioactively label the DNA & RNA fragments for detection or purification. These Radiolabeled nucleotides are typically incorporated ... Simple Method for 3′-Labeling of RNA - Oxford Academic Two methods are commonly used for 3′-end labeling RNA: T4 RNA ligase with 3′,5′ [5′- 32 P]pCp (1,2), and poly (A) polymerase with [α- 32 P]cordycepin 5′-triphosphate (CoTP or 3′-deoxy-ATP) (3,4). Labeling with T4 RNA ligase requires high concentrations of pCp and enzyme, and is less efficient with long RNAs ( 3 ).
Nucleotide Sequence - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics A nucleic acid sequence, the messenger RNA or mRNA, is translated into the protein it encodes by means of transfer RNAs interacting with the ribosomal apparatus. Transfer RNAs bind to three nucleotides at a time and thus divide the nucleic acid sequence into triplet codons, each specifying one amino acid. However, depending on the point at ...

Labeling nucleotide examples
PDF A simple method for 3-labeling of RNA - Molbio labeled nucleotide (dA in these examples). The 3 ′-labeling procedure described above should be useful for a variety of purposes, such as following a 3′ RNA fragment in ribozyme or RNA processing reactions, and the labeling of 5′ blocked RNAs such as mRNAs ( 12 ,13 ). The ability to selectively DNA and RNA Probe Labeling | Radiolabeled Nucleotides Overview. Radiolabeled nucleotides are commonly used for detection of specific nucleic acid sequences. They are typically incorporated enzymatically into DNA and RNA sequences for detection and analysis. Labeled nucleotides may be incorporated by a variety of methods including in vitro transcription with SP6, T3 or T7 RNA polymerase, 3' end ... Fluorescent nucleotides and labeling methods using the same Fluorescent nucleotides useful for labeling nucleic acids which are represented by the formula: X—Y—Z wherein X represents a residue of natural or non-natural nucleotide and the like and binds to Y at a basic moiety of the residue; Y represents a divalent bridging group or a single bond; Z represents a monovalent group derived from a compound represented by the formula (I) wherein R 1 to R ...
Labeling nucleotide examples. Nucleic Acid Labeling - Sepmag Nucleic acids can be labeled using enzymes. The T4 RNA ligase for example helps catalyze a 5'-phosphate attachment to the terminal 3'-hydroxyl on RNA or in some cases it can be optimized to act on single stranded DNA. You can use this enzyme to attach radioactive or chemical labels such as biotin to the 3' end of the RNA. Isotope labeling for studying RNA by solid-state NMR spectroscopy Isotope labeling, either as nucleotide-specific, atom-specific or segmental labeling, can resolve resonance overlaps and reduce the line width, thus allowing ssNMR studies of RNA domains as part of large biomolecules or complexes. ... For example, an E. coli strain deficient in the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase pathway (K10-1516) ... What are some examples of nucleotides? + Example Nucleotide really just means a component of a nucleic acid in which you have 3 components: Ribose sugar, Nitrogenous base, and Phosphate (if you are missing the phosphate, these are called nucleosides. So you can have either DNA or RNA nucleotides. Take the adenosine base as an example. The 5 Kinds of Nucleotides - ThoughtCo For example, a nucleotide that has an adenine base and three phosphate residues would be named adenosine triphosphate (ATP). If the nucleotide has two phosphates, it would be adenosine diphosphate (ADP). If there is a single phosphate, the nucleotide is adenosine monophosphate (AMP). More Than 5 Nucleotides
DNA Labeling - NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified ... Nucleotide: Structure, Examples and Function - BYJUS Nucleosides are named as Adenosine, Guanosine, Thymidine, Cytidine, Uridine Nucleotide = Nucleoside + Phosphate Nucleotides are named as Adenylic acid, Guanylic acid, Thymidylic acid, Cytidylic acid and Uridylic acid. Labeling Oligonucleotides and Nucleic Acids—Section 8.2 These ChromaTide nucleotides are useful for generating labeled nucleic acids for molecular biology and molecular cytogenetics applications, including chromosome and mRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) experiments ( ), gene expression and mutation detection on arrays and microarrays ( Figure 8.2.1 ), and in situ PCR and RT-PCR. nucleotide biology Flashcards and Study Sets | Quizlet Nucleotide nucleic acids RNA A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon sugar cov… DNA and RNA ribonucleic acid; a nucleic acid that plays an important role… 63 terms neslielopez MCAT Nucleotides - Biology Review Nucleotide pentose (sugar) Ribose a compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate gr…
3.3.5 Draw a simple diagram of DNA structure - YouTube Here I demonstrate drawing the structure of DNA. You don't need to be an artist, its relative positions of the phosphate groups, deoxyribose sugar (together known as the sugar-phosphate backbone),... Nucleotide analogs as rigid spin labels for DNA and RNA Benzi-spin is a spin label which differs from most previous examples of rigid spin labels in that rather than being based on a canonical nucleoside, with a specific base pairing partner, it is ... Methods for Labeling Nucleic Acids - Thermo Fisher Scientific The Invitrogen KinaseMax 5' End-Labeling Kit allows the efficient end-labeling of DNA or RNA to high specific activity with T4 polynucleotide kinase and [gamma- 32 P] ATP, or quantitative phosphorylation of 5' ends using unlabeled ATP. The kit includes sufficient reagents for 30 reactions. 5' end-labeling reactions with T4 PNK. Can You Correctly Label Various Parts Of A Dna Molecule Nucleotide Definition Structure 3 Parts Examples Function . Can you correctly label various parts of a dna molecule depends on how much knowledge you have about the dna molecule. Can you correctly label various parts of a DNA molecule. Each of these chains is known as a DNA chain or a DNA strand. This structure is described as a double-helix as ...
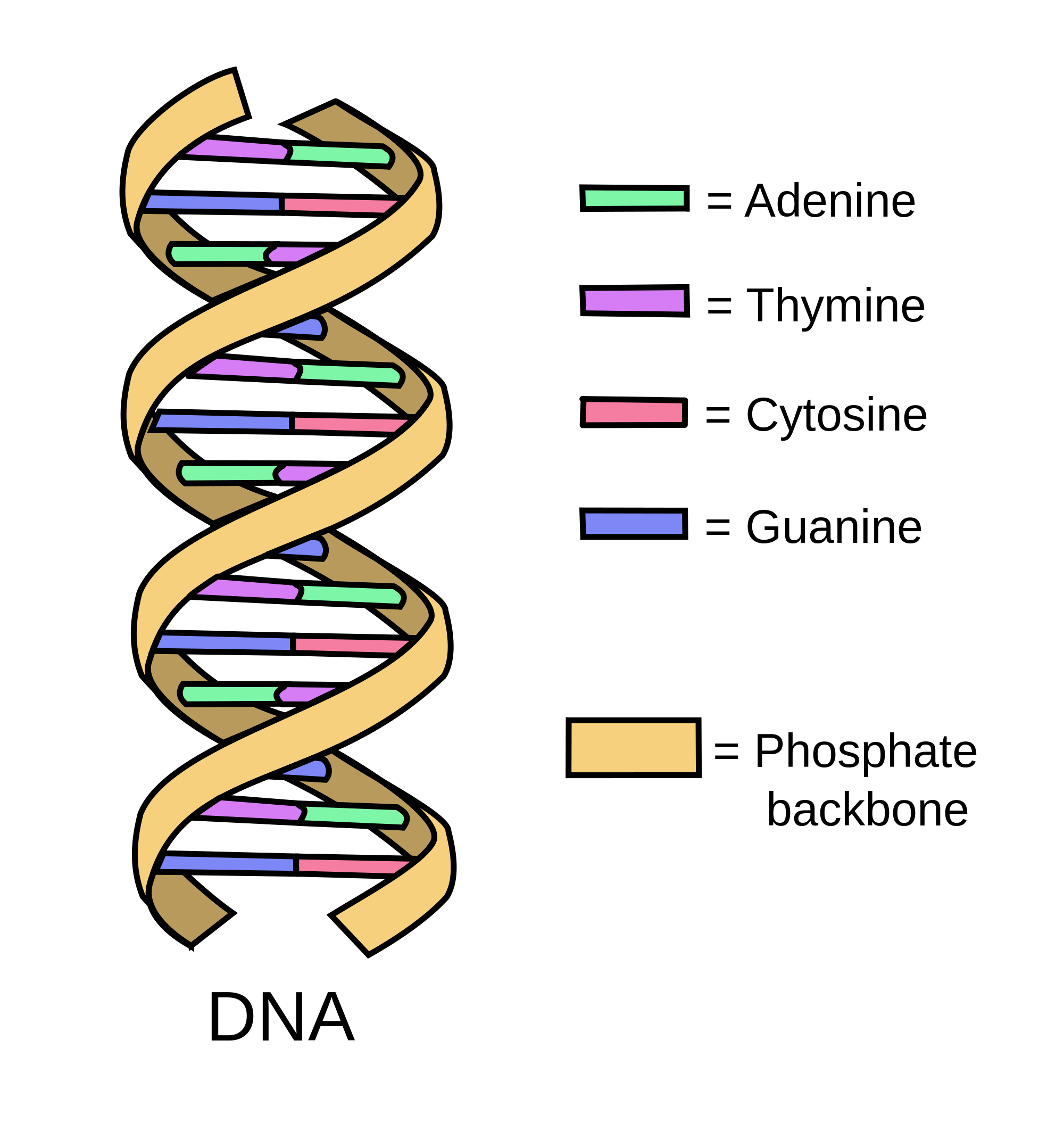
3 Parts of a Nucleotide and How They Are Connected Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are pyrimidines. In DNA, the bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C). In RNA, the bases are adenine, guanine, uracil, and cytosine. Pentose Sugar In DNA, the sugar is 2'-deoxyribose. In RNA, the sugar is ribose. Both ribose and deoxyribose are 5-carbon sugars.
Nucleotide - Definition, Structure (3 Parts), Examples & Function Nucleotide Examples Adenine Adenine is a purine, which is one of two families of nitrogenous bases. Purines have a double-ringed structure. In DNA, adenine bonds with thymine. In RNA, adenine bonds with uracil. Adenosine triphosphate, as discussed earlier, uses the nucleotide adenine as a base. From there, three phosphate groups can be attached.
Manually Labeling Clades on a Nextstrain Tree alt is the nucleotide that the site mutated to. For example if the nucleotide mutation is G9417A, then alt would be A. Note that some clades will be defined by more than one mutation. To avoid any conflicts with other clades, you should list all the mutations in the TSV file (using the same clade name, but different site information).
Nucleotide - Genome.gov A nucleotide is the basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA). A nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA) attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. The bases used in DNA are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T).
Labeling DNA Probes: Radioisotopes, Fluorophores, Biotin ... - JoVE These labels can be incorporated chemically after the synthesis of DNA probes or during their synthesis via one of the two methods. In the end-labeling method, the hydroxyl or phosphate of the nucleotide present at the 5' or 3' termini of the probe DNA sequence is covalently bound to the desired chemical group or label.
dna-labeling | NEB A variety of enzymatic or chemical methods are available to generate nucleic acids labeled with radioactive phosphates, fluorophores, or nucleotides modified with biotin or digoxygenin for example. Nucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end, their 3´ end, or throughout the molecule depending on the application.
Nucleotide Structure: DNA Diagram - Science Trends Nucleotides are made out of elements like nitrogen and carbon with a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar component, and a group of phosphates. However, there are some important differences between RNA nucleotides and DNA nucleotides. The nitrogenous bases come in one of two different forms - they are either a pyrimidine or a purine.
Nucleotides labeled with... - Jena Bioscience Nucleotides labeled with... Biotin Adenosines Guanosines Uridines Cytidines Desthiobiotin Digoxigenin DNP (Dinitrophenol) Photo-labile groups ("Caged") Adenosines Guanosines Xanthosines Triple bonds (Alkyne) DBCO Azide (-N 3) Adenosines Guanosines Uridines Cytidines Thymidines TCO Vinyl Free amino group (-NH 2) Adenosines Guanosines Cytidines
Biotinylated Nucleotides for DNA Labeling - Jena Bioscience Table 1: Enzymatic incorporation of Biotinylated Nucleotides. PCR: Polymerase chain reaction with Taq Polymerase; NT: Nick Translation with DNAse I / DNA Polymerase I; Primer Extension: Primer Extension with Klenow 3'-5'exo-; 3'-End Labeling: Incorporation with Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT); RT:: Reverse Transcription with Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus Reverse Transcriptase (MMLV RT)



Post a Comment for "41 labeling nucleotide examples"