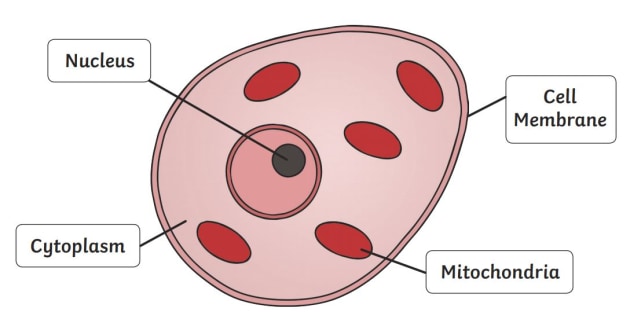
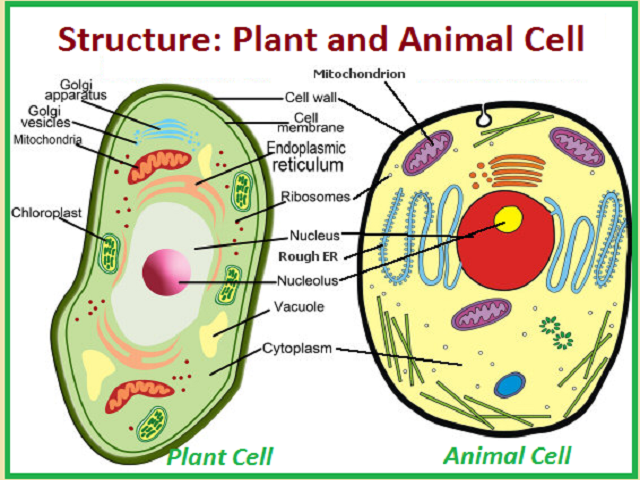
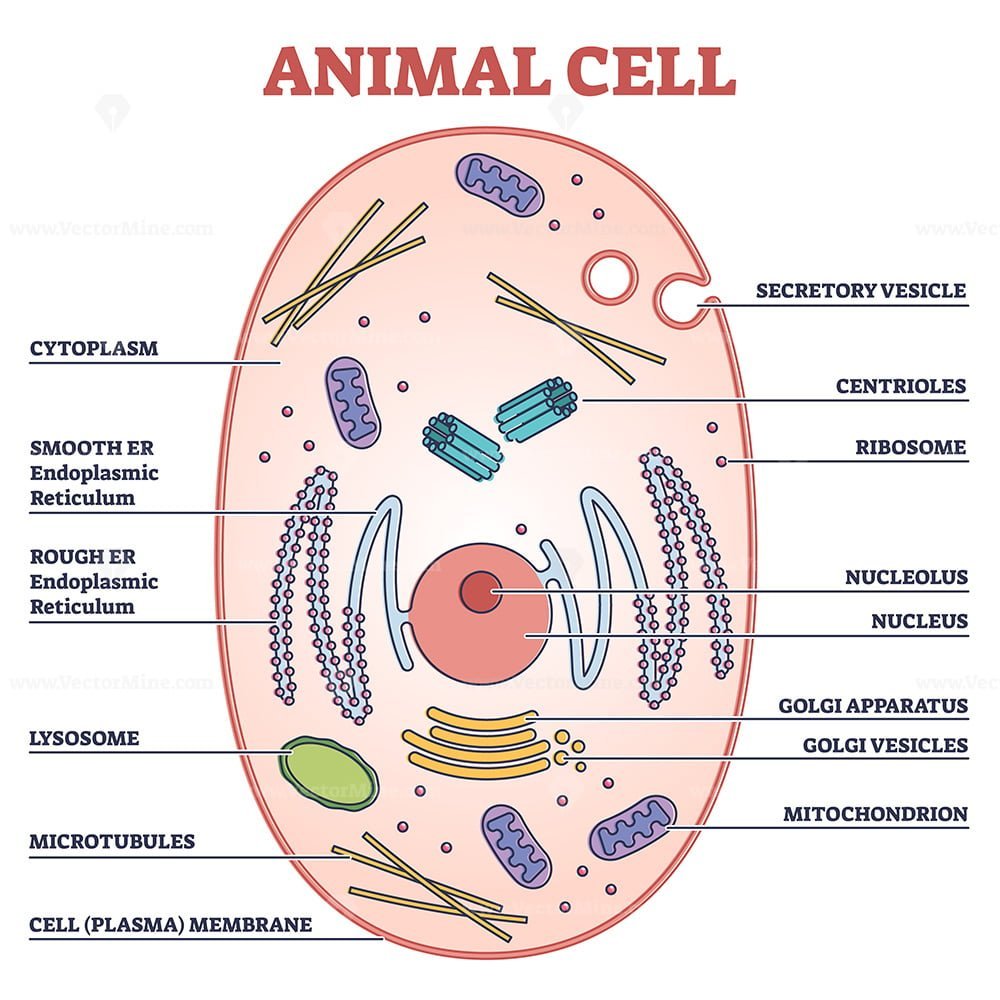
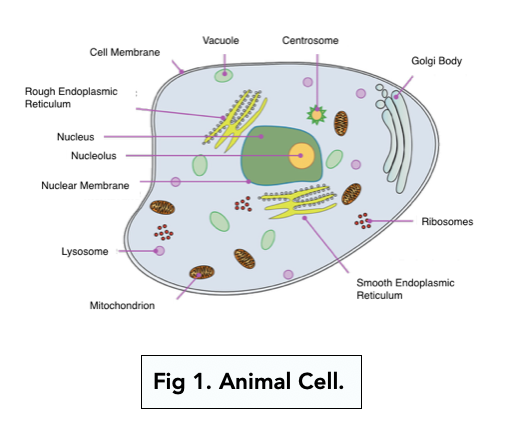
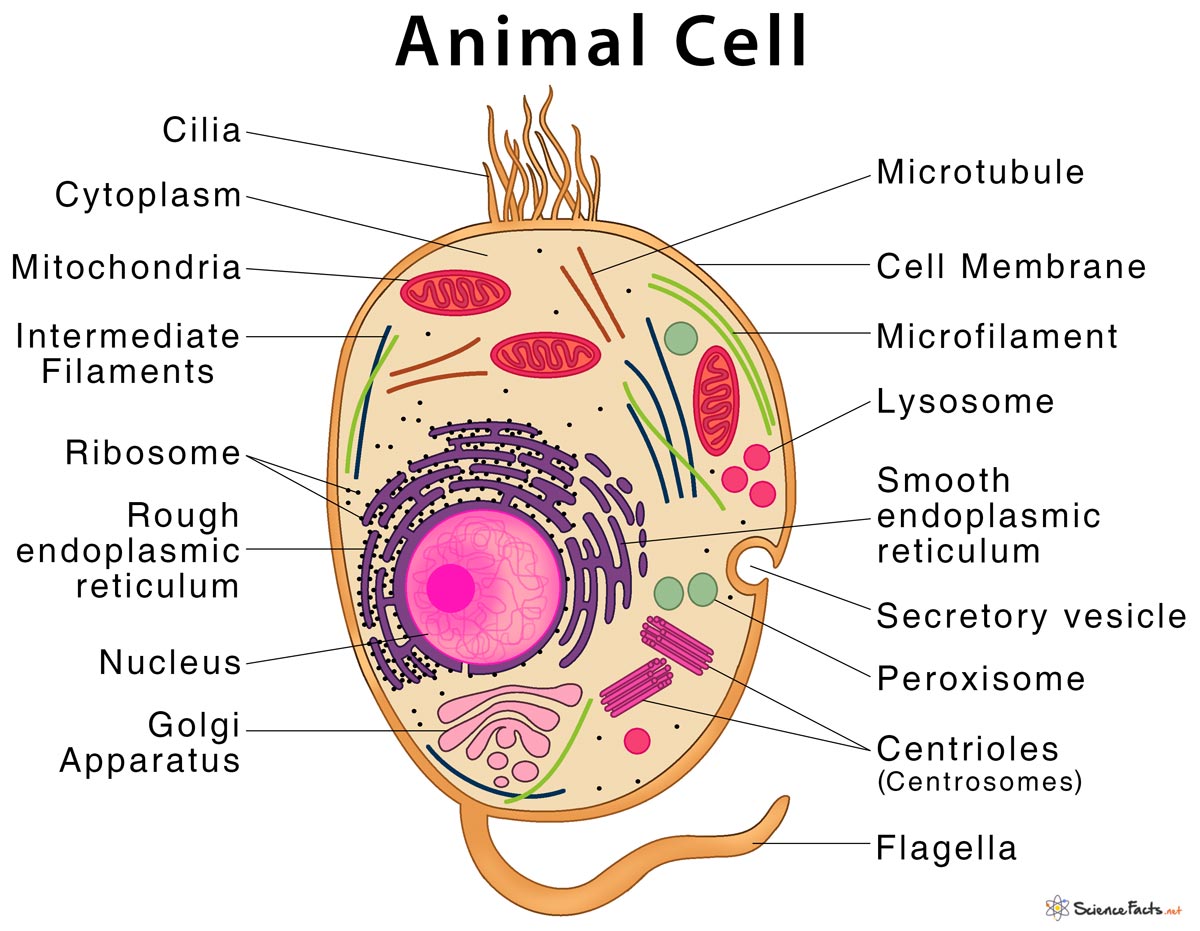
41 animal cell
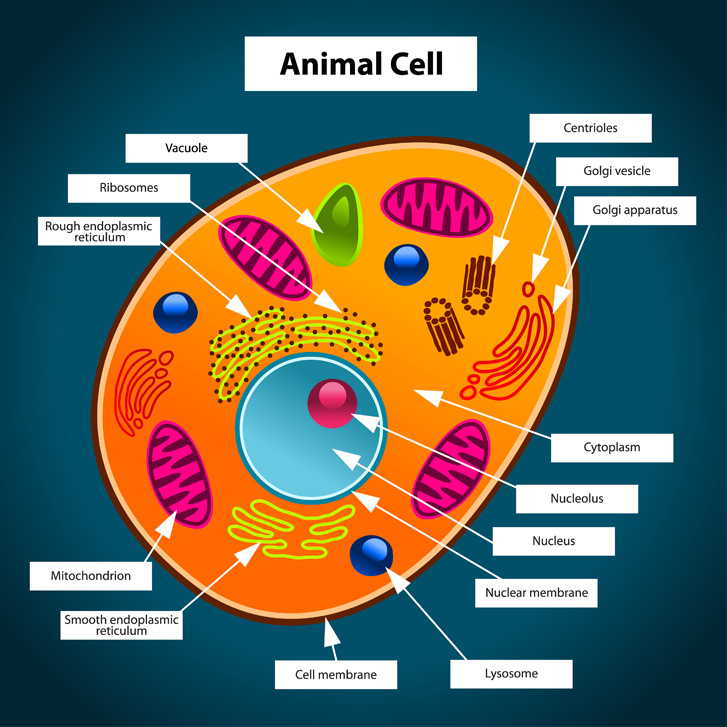
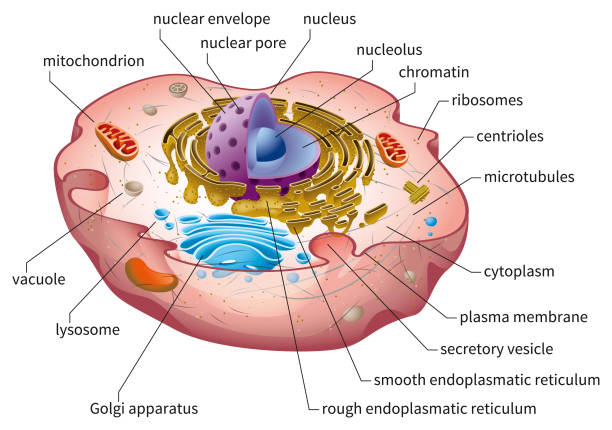
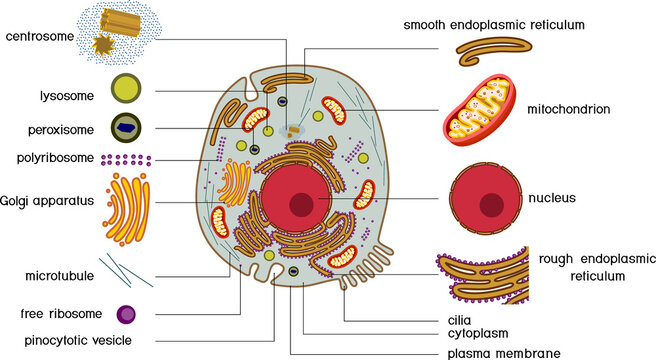
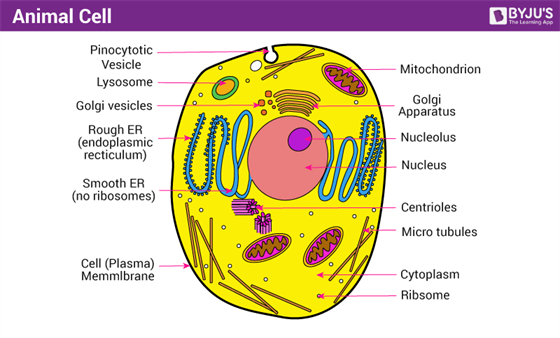
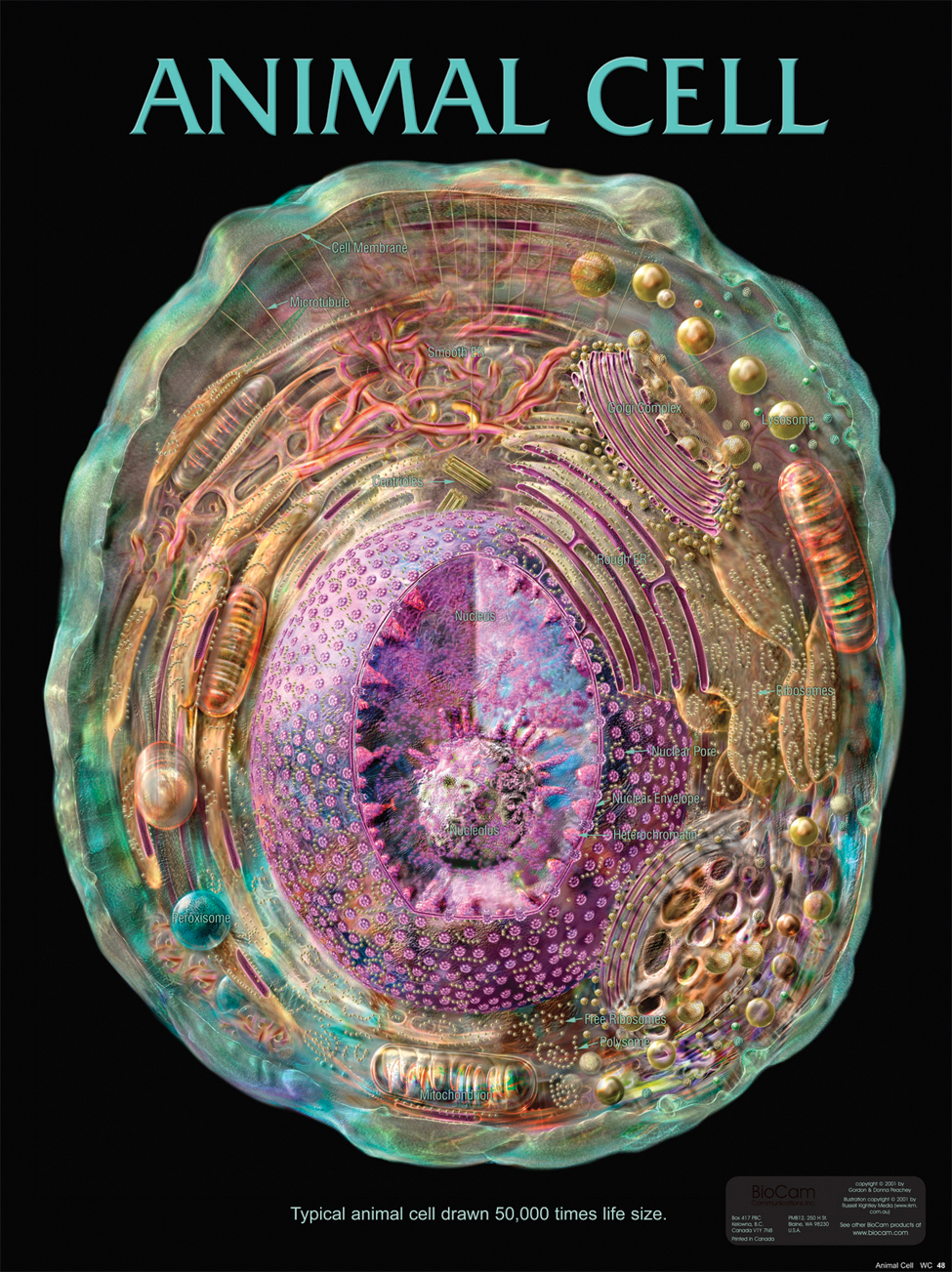
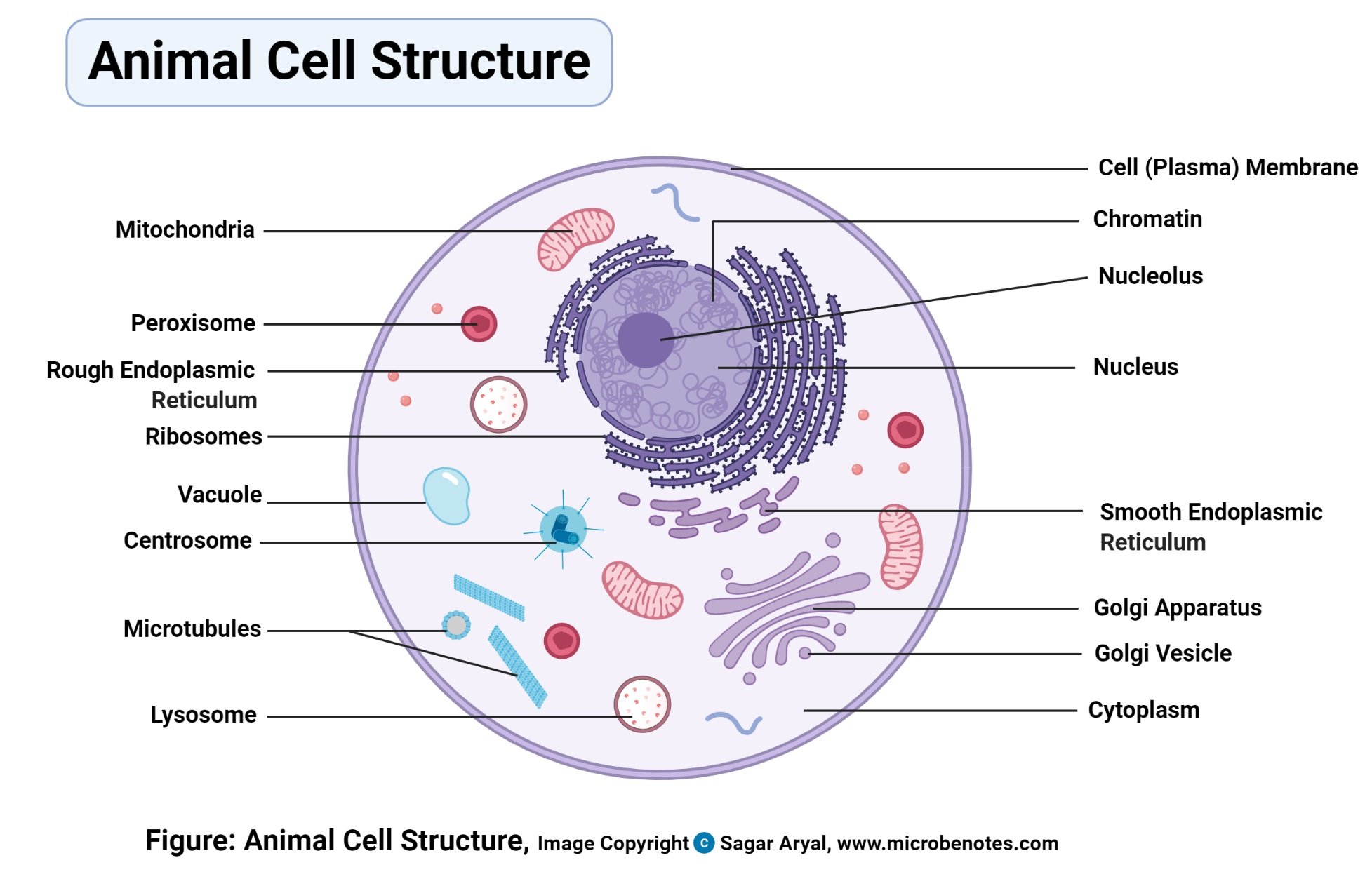
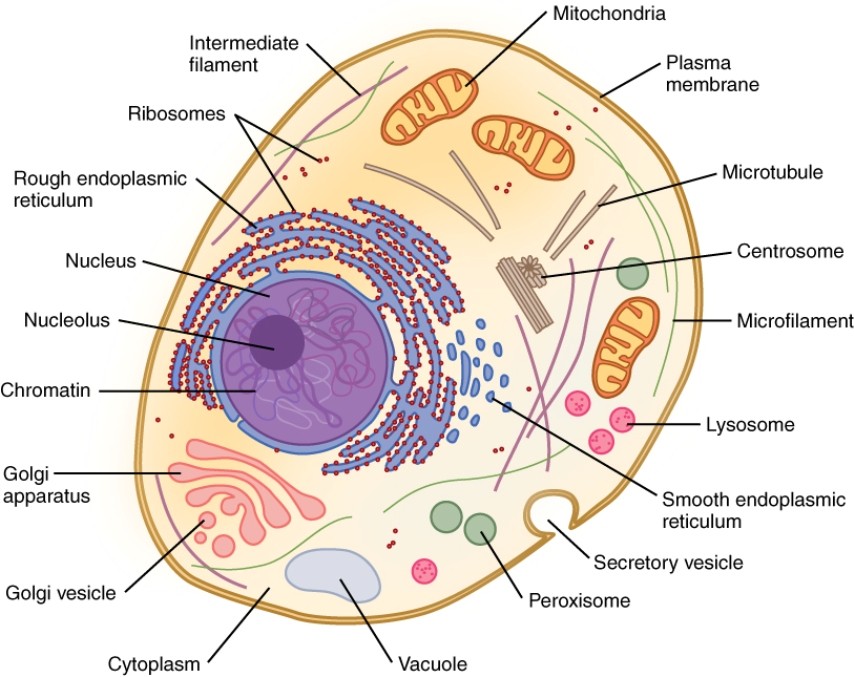
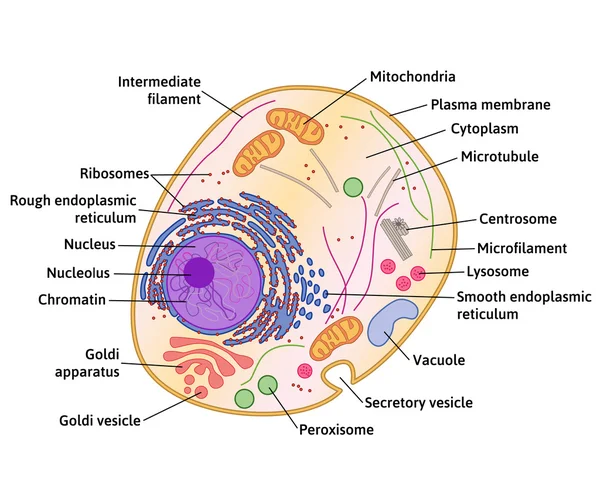
Animal Cells and the Membrane-Bound Nucleus - ThoughtCo Oct 9, 2019 · Animal cells are eukaryotic cells or cells with a membrane-bound nucleus. Unlike prokaryotic cells , DNA in animal cells is housed within the nucleus . In addition to having a nucleus, animal cells also contain other membrane-bound organelles, or tiny cellular structures, that carry out specific functions necessary for normal cellular operation. Animal Cells | Basic Biology General structure of an animal cell. Animal cells have a number of organelles and structures that perform specific functions for the cell. The huge variety of cells that have evolved to fulfill different purposes do not always have all the same organelles or structures, but in general terms, these are some of the structures you can expect to find in animal cells: Plasma membrane
Animal Cell - Structure, Function, Diagram and Types - BYJUS Animal cells range in size from a few microscopic microns to a few millimetres. The largest known animal cell is the ostrich egg, which can stretch over 5.1 inches across and weighs about 1.4 kilograms. This is in stark contrast to the neuron in the human body, which is just 100 microns across. The shape of animal cells also varies, with some being flat, others oval or rod-shaped.
Animal cell
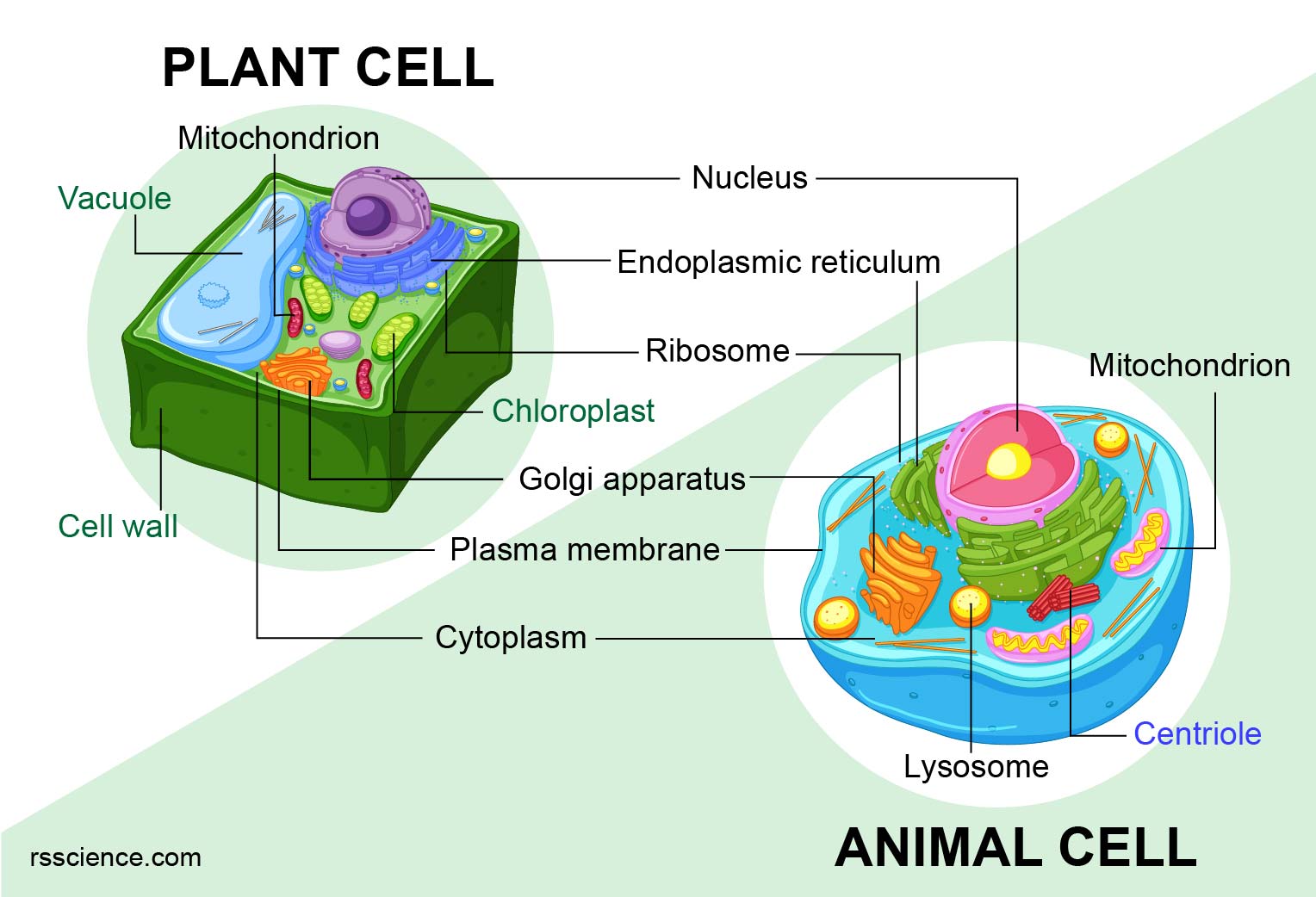
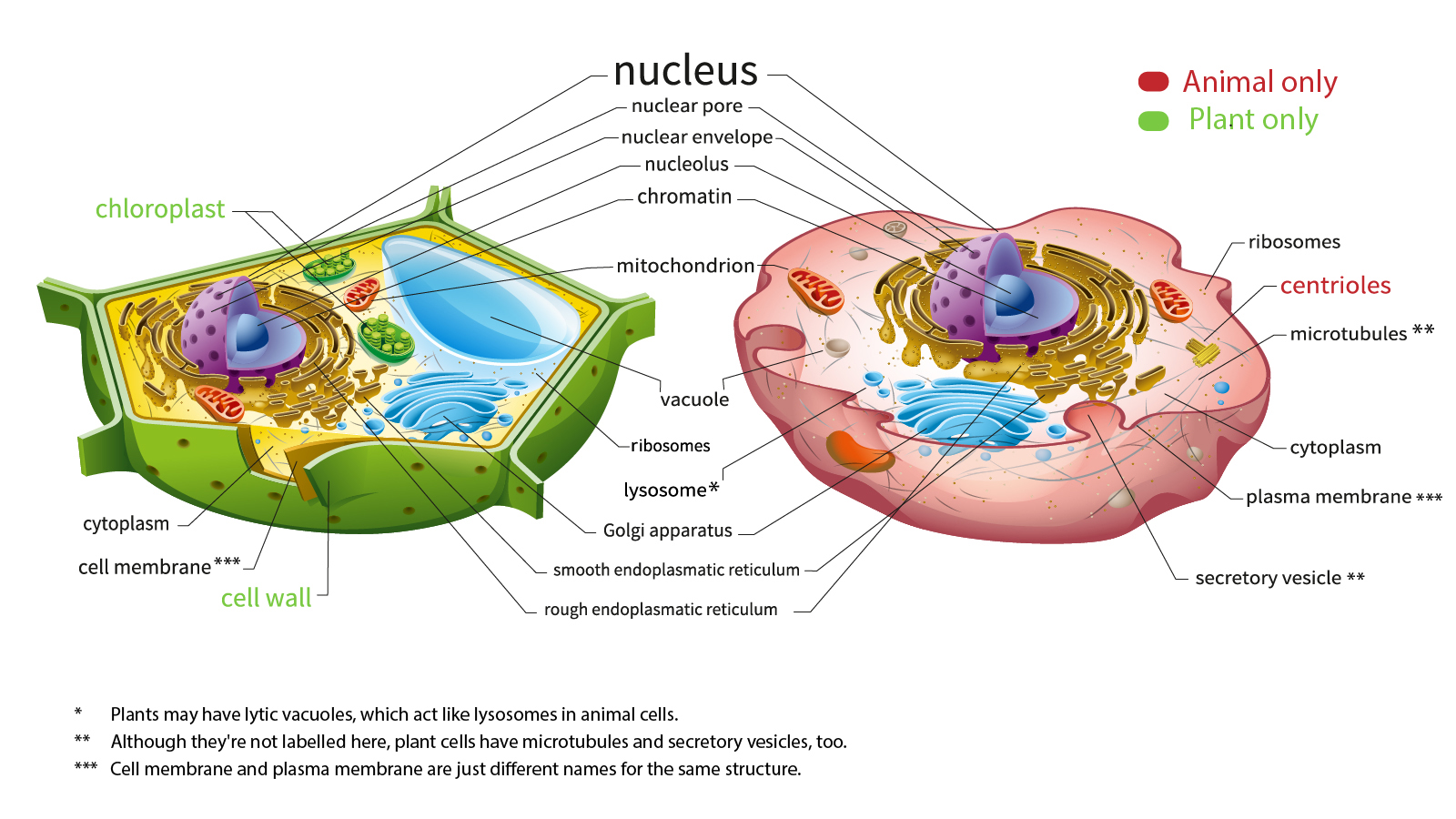
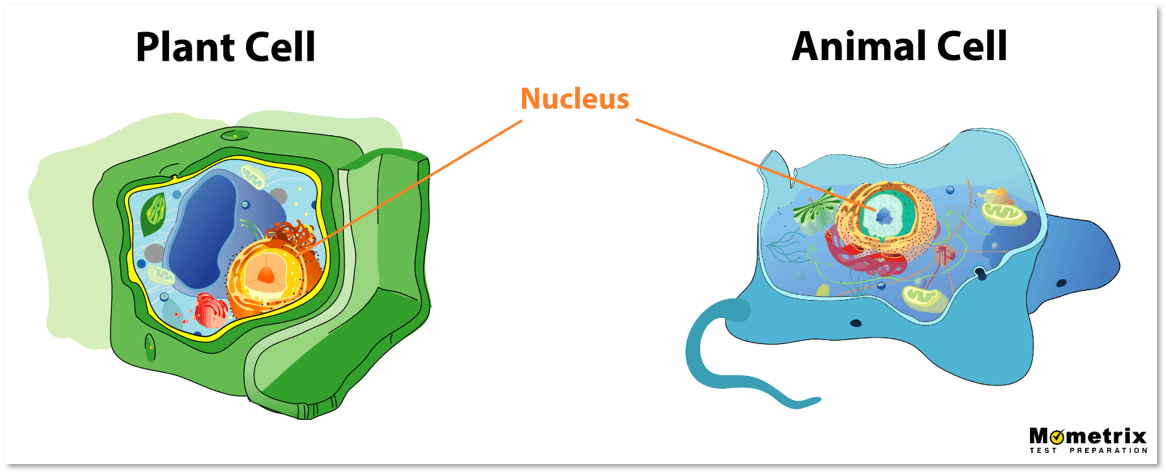
Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Oct 19, 2020 · Animals are all multicellular, meaning multiple cells work together to form the whole organism. In complex organisms, such as humans, these cells can be highly specialized to perform different functions. As such, they often look and function very differently from one another, even though they are all human cells. Plant vs animal cells review (article) | Khan Academy Both plant and animal cells have vacuoles. A plant cell contains a large, singular vacuole that is used for storage and maintaining the shape of the cell. In contrast, animal cells have many, smaller vacuoles. Plant cells have a cell wall, as well as a cell membrane. In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane. Animal Cell: Types, Diagrams and Functions - Embibe Jan 24, 2023 · A group of cells assemble to form tissues, organs, and organ systems. Animal cells vary in different shapes and sizes and perform specific functions. They are considered to be multicellular organisms. Animal cells have an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope. The different animal cells are skin, muscle, blood, nerve and fat cells.
Animal cell. Animal Cell | National Geographic Society A cell is the smallest unit that is typically considered alive and is a fundamental unit of life. All living organisms are composed of cells, from just one (unicellular) to many trillions (multicellular). Cell biology is the study of cells, their physiology, structure, and life cycle. Teach your students about cell biology using these classroom ... Animal Cell: Types, Diagrams and Functions - Embibe Jan 24, 2023 · A group of cells assemble to form tissues, organs, and organ systems. Animal cells vary in different shapes and sizes and perform specific functions. They are considered to be multicellular organisms. Animal cells have an organized nucleus with a nuclear envelope. The different animal cells are skin, muscle, blood, nerve and fat cells. Plant vs animal cells review (article) | Khan Academy Both plant and animal cells have vacuoles. A plant cell contains a large, singular vacuole that is used for storage and maintaining the shape of the cell. In contrast, animal cells have many, smaller vacuoles. Plant cells have a cell wall, as well as a cell membrane. In plants, the cell wall surrounds the cell membrane. Animal Cell - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary Oct 19, 2020 · Animals are all multicellular, meaning multiple cells work together to form the whole organism. In complex organisms, such as humans, these cells can be highly specialized to perform different functions. As such, they often look and function very differently from one another, even though they are all human cells.
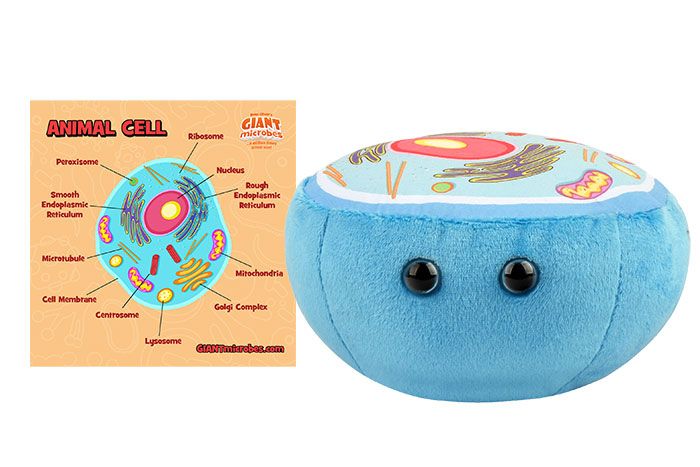


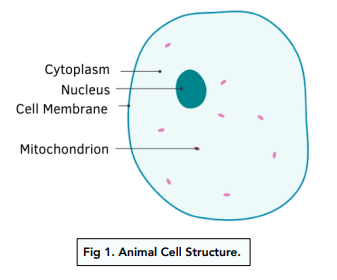
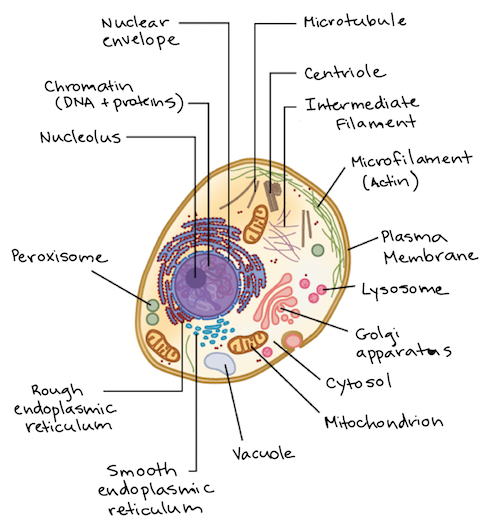
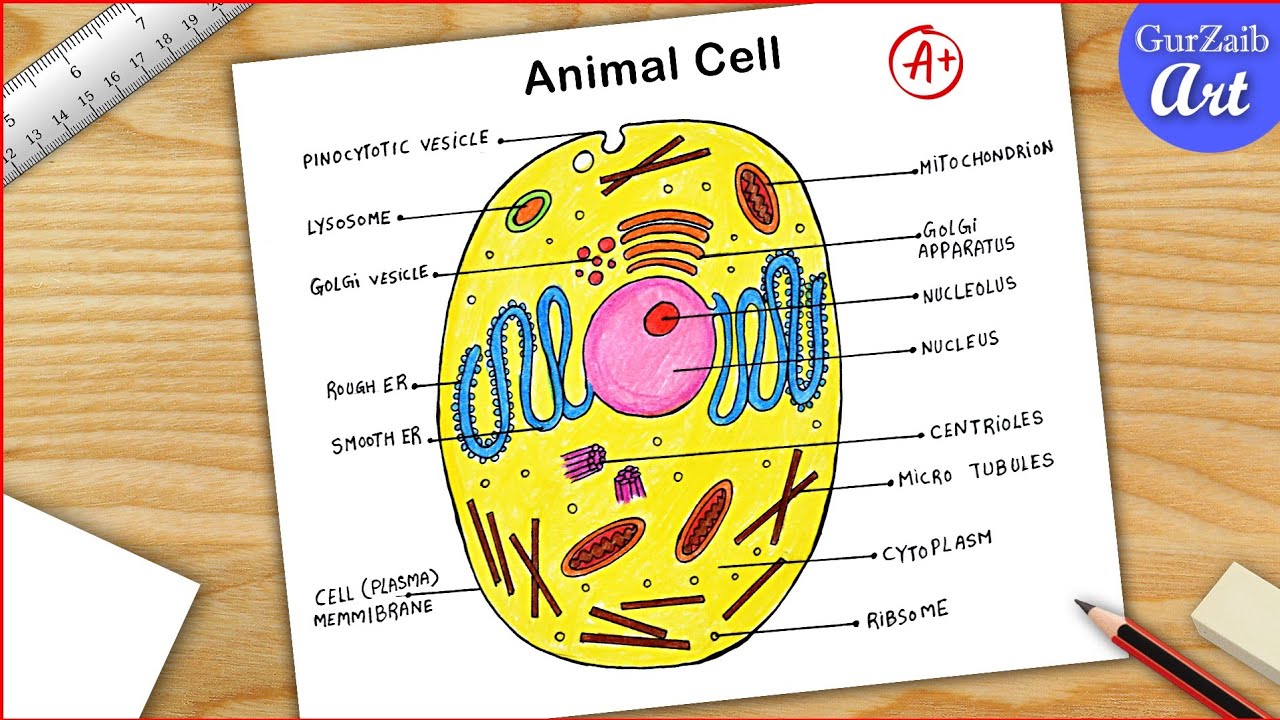
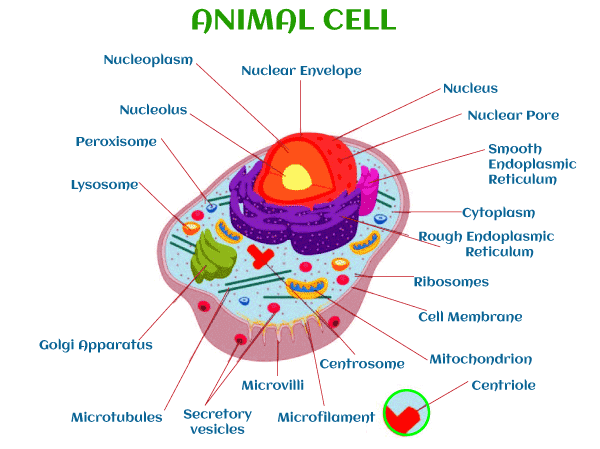



















Post a Comment for "41 animal cell"